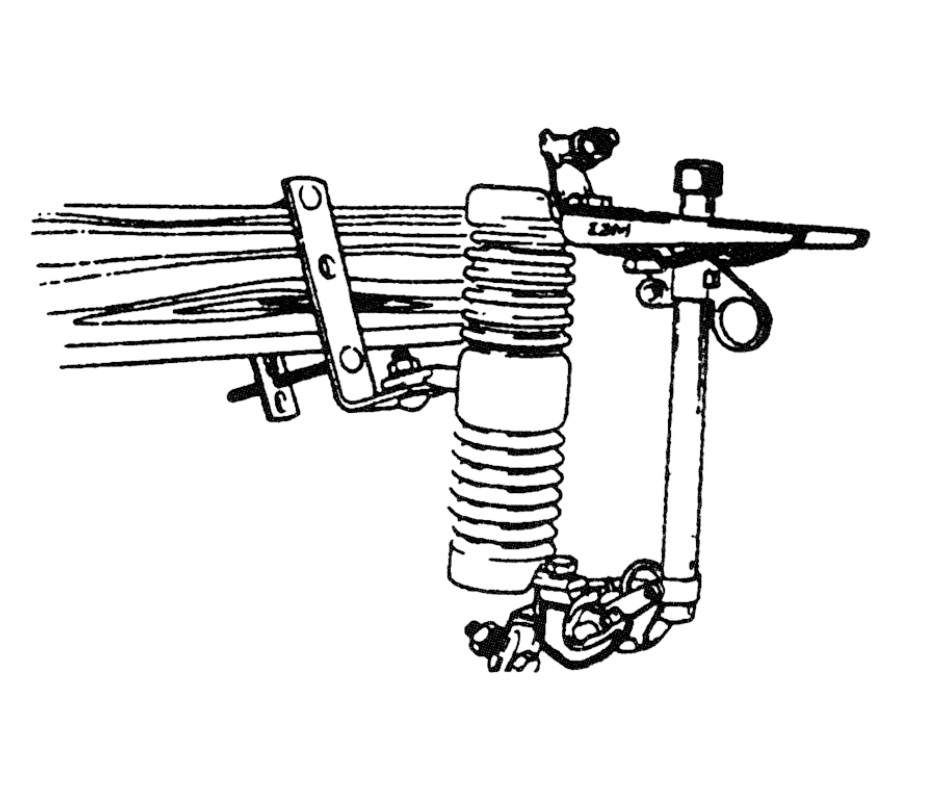
In electrical distribution, a drop out fuse or cut-out fuse is a combination of a fuse and a switch, used in primary overhead feeder lines and taps to protect distribution transformers from current surges and overloads.
A drop-out fuse, or cut-out fuse, is a crucial protective device used in electrical distribution systems, particularly in primary overhead feeder lines and taps. Its primary function is to protect distribution transformers from the detrimental effects of current surges and overloads, which could otherwise cause damage or malfunction to the system. The device integrates both a fuse and a switch, enabling it to disconnect the circuit automatically when a fault occurs, thus preventing further damage and ensuring the continuity of the distribution network.
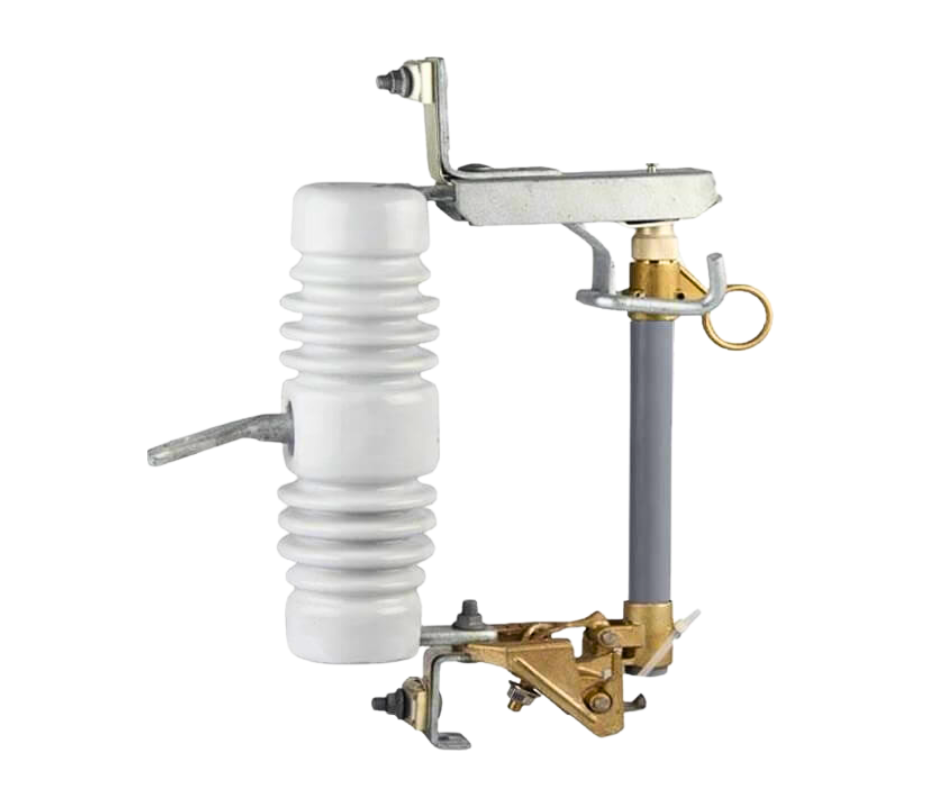

Drop Out Fuse | |||
|---|---|---|---|
Rated Voltage (Normal) | 11KV | Rated Maximum Voltage | 15KV |
Rated Frequency | 50Hz | Bill | 75KV |
Rated Current (RMS) | 100A | ||
Interrupting Current (RMS) | 10KV |
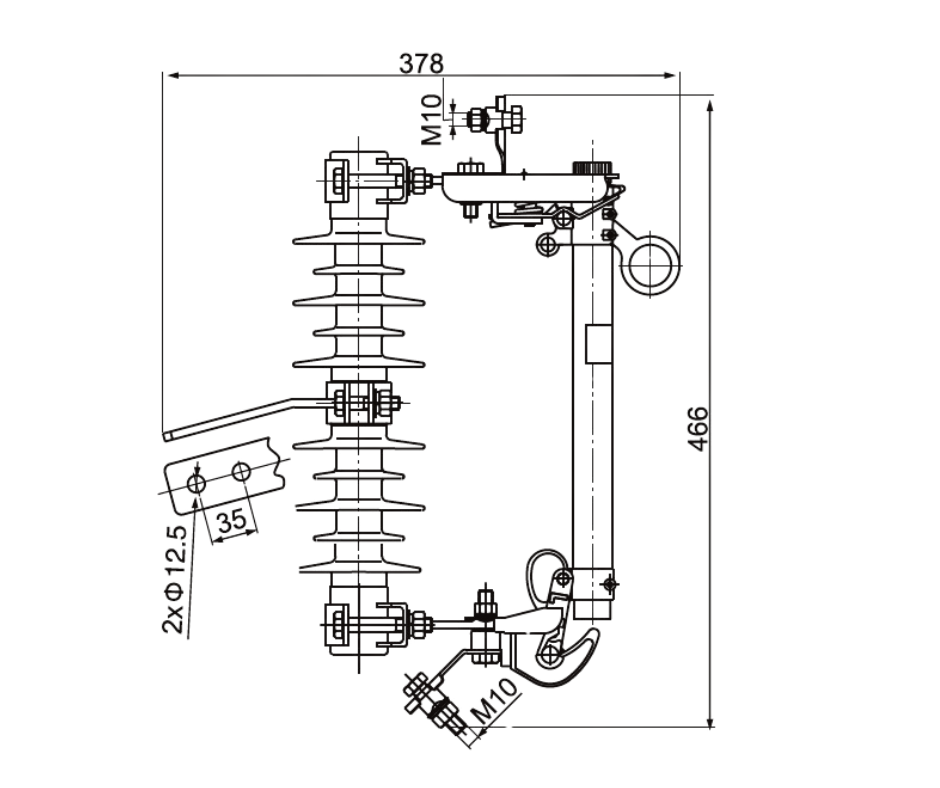
This fuse is designed to handle normal operating conditions with a rated voltage of 11 kV, while it can withstand a maximum voltage of up to 15 kV, making it suitable for high-voltage applications.
The device operates at a rated frequency of 50 Hz, ensuring compatibility with standard power distribution systems. The drop-out fuse is rated for a continuous current of 100A (RMS), meaning it can safely handle currents up to this value without risk of failure. In the event of a fault, it is capable of interrupting currents up to 10 kV (RMS), providing high-performance protection for the electrical infrastructure.
The fuse is designed to drop out or disconnect from the circuit when a fault occurs, providing a visual indication of the fault and simplifying the process of maintenance and restoration. Its robust construction and reliable performance make it a key component in maintaining the stability and safety of electrical distribution networks, especially in remote or hard-to-reach areas where manual intervention would be challenging.